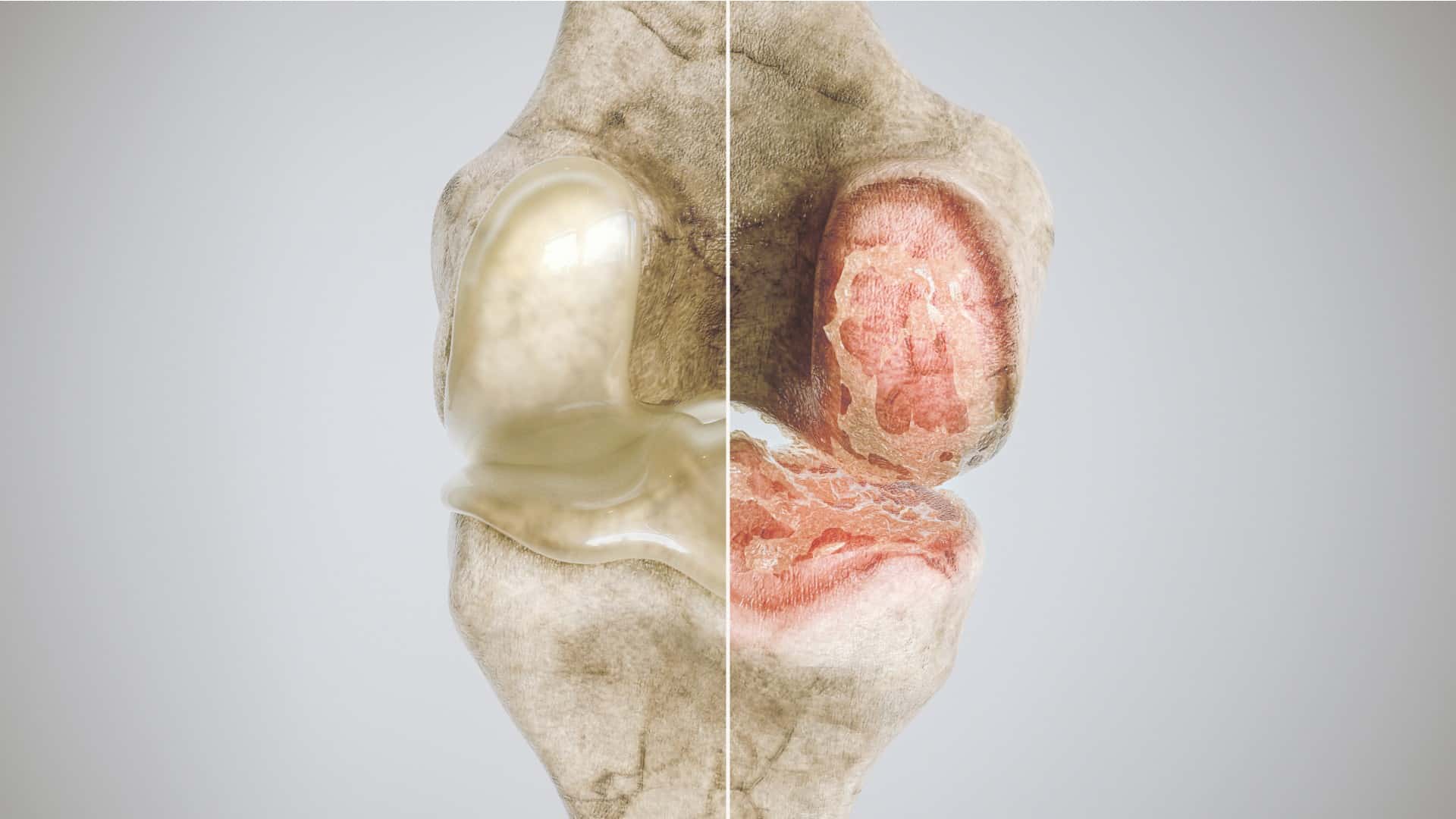
Without your joints, you wouldn't be able to walk, stretch, bend over or perform most of the movements you do each day. Unfortunately, about 25% of American adults have been diagnosed with osteoarthritis, a condition that causes the joints to break down over time. As osteoarthritis worsens, it can lead to joint pain, stiffness and swelling, making everyday activities more difficult.
When osteoarthritis affects the knee, it can be difficult to walk, run, use stairs or engage in other activities requiring the use of your legs. The good news is that several treatment options are available to reduce discomfort and help you get moving again.
Oral Medications

Many people take over-the-counter pain relievers or nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) to manage their knee osteoarthritis symptoms. Acetaminophen, a common pain reliever, blocks the production of prostaglandins — chemicals that trigger inflammation in the human body. If you use acetaminophen to control osteoarthritis pain, it's important to follow the dosing instructions carefully. Taking more than recommended increases the risk for liver damage, especially if you take it with alcohol.
Ibuprofen and naproxen are two of the most common NSAIDs available without a prescription. These medications block an enzyme that's needed to make prostaglandins, reducing inflammation and pain. Although NSAIDs are effective, they shouldn't be used for more than 10 days without approval from a health care provider. NSAIDs may cause heartburn, nausea, stomach pain, vomiting and other side effects. You can prevent or reduce the severity of these side effects by taking each dose with food.
Topical Medications

If oral medications aren't effective or you're concerned about the potential side effects, topical medications are another option. These medications are applied directly to the affected area and absorbed through the skin, preventing upset stomach and other gastrointestinal side effects associated with NSAIDs. Topical medications are especially helpful for knee osteoarthritis because the knee joint is close to the surface of the skin, allowing the medication to travel quickly to the site of the inflammation.
Several topical medications are used for osteoarthritis of the knee and other joints:
- Anesthetics: Anesthetics reduce pain by numbing the affected area. These medications come in several forms, including patches, creams and gels.
- Counterirritants: A counterirritant doesn't take the pain away, but it changes the way you sense pain, reducing the discomfort associated with knee osteoarthritis. This type of medication typically contains camphor or menthol.
- Salicylates: Salicylates contain the same active ingredient as aspirin, so they reduce inflammation and relieve pain when applied topically.
- Capsaicin: Capsaicin creams and patches contain a chemical that prevents the nerve cells from sending pain signals, minimizing the discomfort of knee osteoarthritis.
Injections
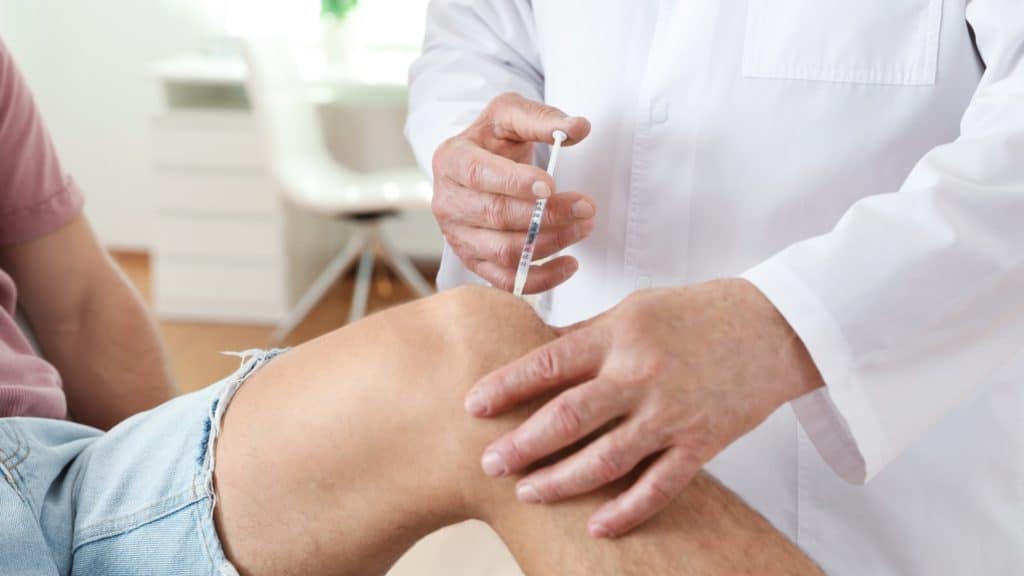
If over-the-counter medications don't relieve your osteoarthritis pain, you may want to try injections of corticosteroids or hyaluronic acid. Corticosteroid injections relieve pain by reducing inflammation around the knee joint. Depending on the location of your symptoms, a corticosteroid injection may be administered directly into the knee or into the tissues surrounding the knee.
Synovial fluid lubricates the joints and makes it easier to move them. There's less synovial fluid around the knee joint in people with osteoarthritis, increasing friction and accelerating arthritis-related wear and tear. A minimally invasive procedure known as viscosupplementation relieves arthritis symptoms by making it easier for the remaining synovial fluid to lubricate the knee joint.
During this outpatient procedure, a health care professional numbs the treatment area, injects hyaluronic acid into the joint and covers the injection site with a bandage. Viscosupplementation usually takes less than an hour, and some patients report reduced pain within as little as five weeks.
Lifestyle Changes

Excess weight puts additional stress on the knees, accelerating arthritis-related damage. If you're above your ideal weight, your doctor may recommend exercise and a balanced diet to shed excess pounds. Even if you're within the recommended weight range for someone of your height and body type, exercise can help with knee arthritis by strengthening the muscles around the affected joint. Working with a physical therapist can help you learn how to exercise safely without making your arthritis symptoms worse or injuring another part of your body.
Surgical Procedures
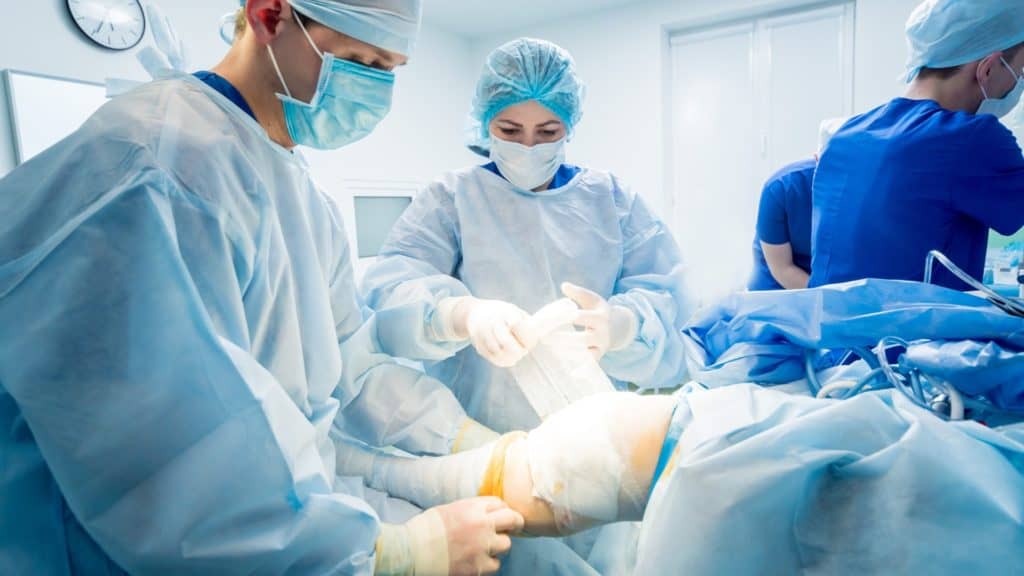
If conservative treatments aren't effective, you may benefit from surgery to remove damaged tissue or replace the worn joint with an artificial one. Arthroscopy and arthroplasty are two procedures used to treat knee osteoarthritis that hasn't responded to other treatment methods.
Arthroscopy
Arthroscopy is a minimally invasive procedure used to examine the knee joint. During this procedure, a physician makes several small incisions in the knee. These incisions are much smaller than a traditional surgical incision, reducing postsurgical pain and making it easier to recover. After making these incisions, the physician uses an arthroscope to look at the knee joint. In some cases, additional tools are used to remove damaged cartilage or clean the surface of the bone.
Most people go home about 2 hours after the procedure. If you have pain after the surgery, your doctor may recommend taking NSAIDs or other pain relievers. You may also need to take aspirin to reduce the risk of blood clots at the surgical site. It typically takes about six to eight weeks to recover completely from arthroscopy.
Arthroplasty (Joint Replacement)
For people with severe knee osteoarthritis, joint replacement offers the best chance at relief. During this procedure, a surgeon removes the damaged joint and replaces it with a prosthesis made from a combination of titanium and other elements. If you have your knee joint replaced, you'll likely stay in the hospital for several days afterward.
While admitted, you'll receive around-the-clock nursing care and work with a physical therapist to start regaining function in the affected leg. Following your discharge from the hospital, you may need to attend physical therapy sessions or have a physical therapist come to your home. It's important to keep moving after your surgery, as too much sitting down or lying in bed can make your pain and stiffness worse.
Expert Help for Knee Osteoarthritis

Knee osteoarthritis can interfere with your job or make it difficult to enjoy your favorite hobbies, but there's a lot you can do to manage your symptoms. If over-the-counter medications aren't helping, contact Northeast Spine and Sports Medicine at (732) 653-1000.